A mercury manometer is connected to an air duct, providing a reliable and accurate method for measuring air pressure. This essential tool plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, ensuring efficient and comfortable indoor environments.
Composed of a U-shaped glass tube filled with mercury, a mercury manometer operates on the principle of fluid mechanics. When connected to an air duct, the pressure difference between the duct and the atmosphere causes the mercury to move within the tube, creating a height differential that corresponds to the pressure being measured.
Understanding the Components and Functions: A Mercury Manometer Is Connected To An Air Duct
A mercury manometer consists of a U-shaped glass tube partially filled with mercury. The tube is connected to an air duct at one end and open to the atmosphere at the other. When air flows through the duct, it creates a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube, causing the mercury level to rise on one side and fall on the other.
The difference in mercury levels indicates the air pressure in the duct.
Connecting to an Air Duct
Connecting a mercury manometer to an air duct requires careful consideration. The connection method should ensure a leak-free seal and allow for accurate pressure measurement. The most common methods are using a rubber tube, a plastic adapter, or a direct connection to a tapping point on the duct.
Measuring Pressure in an Air Duct
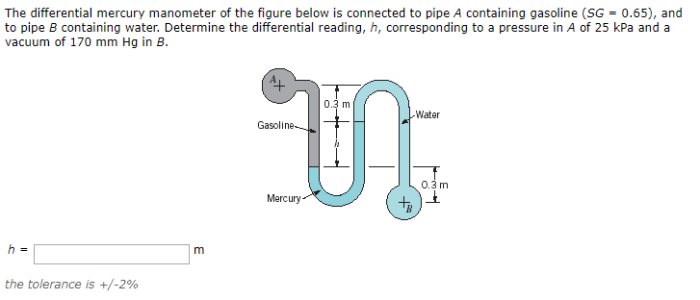
To measure air duct pressure using a mercury manometer, follow these steps:
- Connect the manometer to the air duct using an appropriate method.
- Open the valve to allow air to flow through the duct.
- Read the difference in mercury levels between the two sides of the tube.
- Record the pressure reading and compare it to the desired value.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
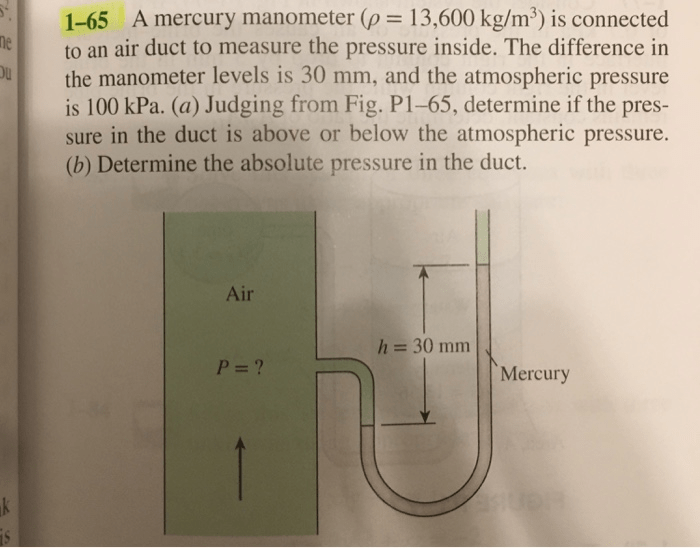
Interpreting the readings obtained from a mercury manometer requires understanding the principles of pressure measurement. The pressure difference indicated by the mercury level difference is equal to the pressure difference between the air duct and the atmosphere. Factors that can affect the accuracy of the readings include the temperature of the mercury, the diameter of the tube, and the presence of leaks.
Applications in HVAC Systems
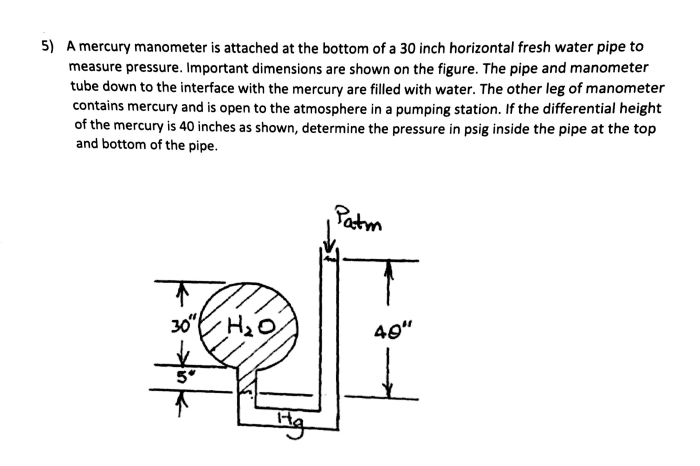
Mercury manometers are widely used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to measure air duct pressure. Accurate pressure measurements are essential for optimizing HVAC performance, ensuring proper airflow, and maintaining indoor air quality.
Limitations and Alternatives

Mercury manometers have limitations, including environmental concerns due to the toxicity of mercury and accuracy constraints at low pressure ranges. Alternative methods for measuring air duct pressure include digital pressure gauges, inclined manometers, and pitot tubes. These alternatives offer advantages such as improved accuracy, ease of use, and reduced environmental impact.
General Inquiries
What are the advantages of using a mercury manometer?
Mercury manometers offer high accuracy, reliability, and durability. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to use.
What are the limitations of mercury manometers?
Mercury is a toxic substance, posing environmental and health concerns. Mercury manometers can be affected by temperature changes and vibrations.
What are some alternative methods for measuring air duct pressure?
Digital pressure gauges, inclined manometers, and pitot tubes are alternative methods that offer varying degrees of accuracy and convenience.