Rank these electromagnetic waves on the basis of their frequency, an in-depth exploration into the fascinating world of electromagnetic waves and their diverse applications. This comprehensive analysis delves into the concept of frequency, categorizes different types of electromagnetic waves, and presents a comparative table to illustrate their frequency ranges.
Moreover, it examines the practical implications and technological advancements driven by the understanding of electromagnetic wave frequencies, providing a holistic understanding of this fundamental aspect of physics.
Electromagnetic waves encompass a vast spectrum, from low-frequency radio waves to high-energy gamma rays, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the frequency-based ranking of these waves is crucial for harnessing their potential and shaping future technological advancements.
Frequency Range and Spectrum: Rank These Electromagnetic Waves On The Basis Of Their Frequency
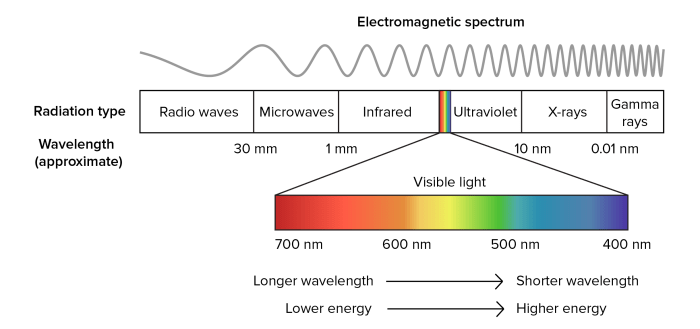
Electromagnetic waves are characterized by their frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz). The frequency of a wave refers to the number of oscillations it undergoes per second. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of frequencies, from extremely low frequencies (ELF) to extremely high frequencies (EHF).
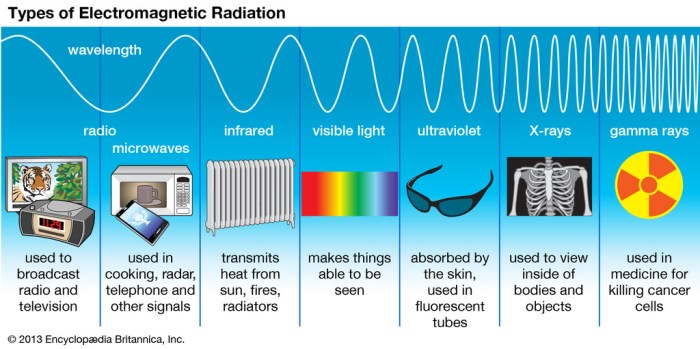
The electromagnetic spectrum can be visually represented as a continuous band of frequencies, with each frequency range corresponding to a different type of electromagnetic wave. The spectrum can be divided into several regions, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Types of Electromagnetic Waves, Rank these electromagnetic waves on the basis of their frequency
- Radio Waves:Frequencies ranging from 3 Hz to 300 GHz, used for communication, navigation, and remote control.
- Microwaves:Frequencies ranging from 300 GHz to 300 THz, used in microwave ovens, radar systems, and satellite communications.
- Infrared Radiation:Frequencies ranging from 300 THz to 400 THz, used in heat lamps, thermal imaging, and remote sensing.
- Visible Light:Frequencies ranging from 400 THz to 790 THz, the range of electromagnetic waves that can be perceived by the human eye.
- Ultraviolet Radiation:Frequencies ranging from 790 THz to 30 PHz, used in tanning beds, sterilization, and phototherapy.
- X-Rays:Frequencies ranging from 30 PHz to 300 EHz, used in medical imaging, security scanners, and industrial applications.
- Gamma Rays:Frequencies above 300 EHz, the highest energy electromagnetic waves, used in cancer treatment, sterilization, and scientific research.
Frequency Comparison
| Type of Electromagnetic Wave | Frequency Range |
|---|---|
| Radio Waves | 3 Hz
|
| Microwaves | 300 GHz
|
| Infrared Radiation | 300 THz
|
| Visible Light | 400 THz
|
| Ultraviolet Radiation | 790 THz
|
| X-Rays | 30 PHz
|
| Gamma Rays | >300 EHz |
FAQ Corner
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum refers to the entire range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, encompassing radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
How are electromagnetic waves classified?
Electromagnetic waves are classified based on their frequency, which determines their wavelength and energy. The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into various frequency bands, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What are the applications of different electromagnetic waves?
Different electromagnetic waves have unique applications depending on their frequency. Radio waves are used for communication, microwaves for heating and radar, infrared radiation for thermal imaging and remote sensing, visible light for vision and photography, ultraviolet radiation for disinfection and sterilization, X-rays for medical imaging and security screening, and gamma rays for cancer treatment and industrial radiography.